Oxi-combustion
Ultra-low emission combustion in alternative engines
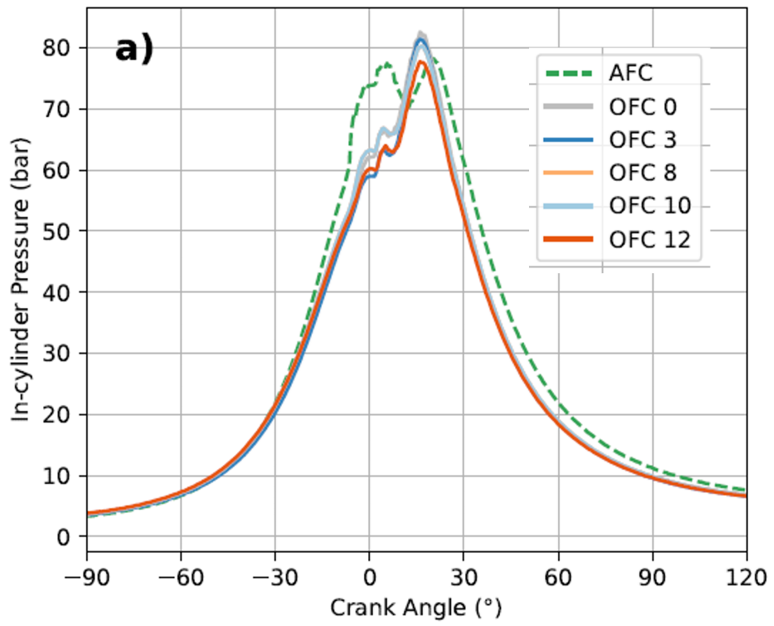
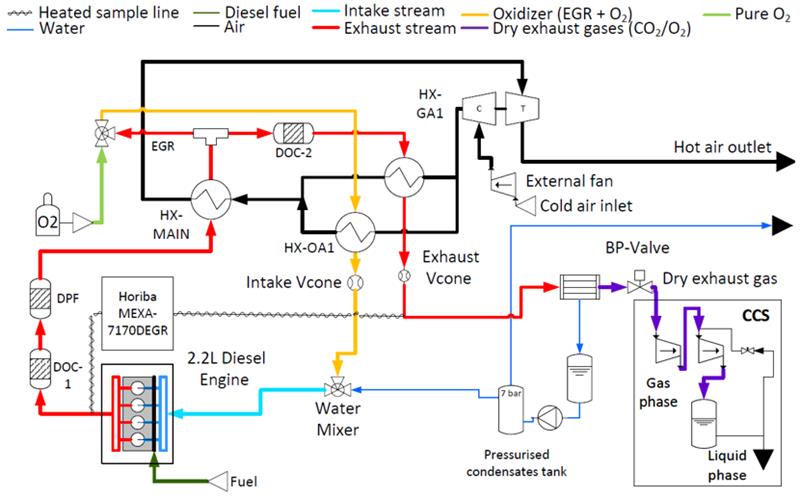
The development of engines operated with oxy-combustion makes it possible to have power generation plants without emissions of nitrogen oxides. In addition, the exhaust gases produced can be treated to capture the CO2 generated during combustion with a high degree of purity. The system is flexible to the use of different fuels, both conventional and second- and third-generation biofuels or synthetic fuels.